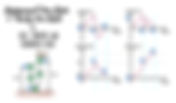370 results found with an empty search
- Various graphs of a simple pendulum and vertical oscillating object
As the reference height is at B, so above that reference height is considered positive, and below the reference height it is considered negative. Hence the height-time graph is as such. Consider a vertical oscillating object, similar to the simple pendulum, the middle is the fastest.
- 2016 PPP1Q3 Initial acceleration and terminal velocity of heavier object
Answer: Option C View the video for explanation
- Keeping the square wooden plane in equilibrium
Answer: Option A View the video for explanation
- Pendulum - What is the period based on the height-time graph
Answer: Option D View the video for explanation
- 2016PPP1Q5 Camera in space station orbiting the Earth
Answer: Option A Many have the misconception that as the astronaut and camera are floating and weightless, there is no gravitational force acting on them. Actually both are inside the gravitational field of the Earth, and there is gravitational field strength, hence there is gravitational force acting on them towards the Earth. But as together with the station, they are all ‘free falling’, hence no normal contact force on the astronaut and camera, hence give the feeling of weightlessness. View the video for the explanation.
- How to make the image formed on the screen sharp?
To get a sharp image on the screen, there are various methods and concepts that you have learned and can be applied here. View the video for the explanation:
- Circuit Breaker - Analyse the diagram to understand how it operates 2022PPp2q10 and 2024PPp2q11
The diagram of circuit breaker may vary. So it is important that you analyse the structure of the circuit breaker in the diagram to understand how it works. The following are two examples of circuit breaker where the structures are different, but the basic working principles are the same. Video explanation part 01: 2022PPp2q10 2022PPp2q10 Suggested answers: Video explanation part 02: 2024PPp2q11 2024PPp2q11 Suggested answers:
- Why charging your EV with a wall socket is not advisable?
There is a related question in Pure Physics 2021 P2 Q9, but slightly different. It asked about why home circuit of 230V is not suitable to power a fast charger like those big size DC charger we see in industrial or shopping malls carpark.
- Velocity-time graph of ball thrown up with air resistance - Part 2
Refer to the video below for the explanation. Related post: Velocity-time graph of ball released from rest with air resistance - Part 1 https://youtu.be/ccWnKbjkezc https://youtu.be/clD1b1i7yX0 https://youtu.be/en2RM_Z14AU https://youtu.be/JuK9pHHa-kk
- Displacement-time and Velocity-time graph when ball is dropped and it rebounces (no energy lost) - Part 01
Refer to the video below for explanation. When a ball dropped and then it re-bounces, the motion varies. This video will cover how the various graphs are sketched and why. In this ideal situation, you ignore air resistance and assume no energy converted to other forms as the ball hits the floor. View the two related videos below https://youtu.be/clD1b1i7yX0 https://youtu.be/en2RM_Z14AU https://youtu.be/JuK9pHHa-kk
- Displacement-time and Velocity-time graph when ball is dropped and it rebounces - with energy lost - Part 02
Refer to the video below for the explanation. When a ball is dropped and it rebounces back, the motion varies. This video will cover how the various graphs are sketched and why when in reality, there is energy lost and the ball not be able to reach the original release hieght. View these related two videos below. https://youtu.be/clD1b1i7yX0 https://youtu.be/en2RM_Z14AU https://youtu.be/JuK9pHHa-kk
.png)