370 results found with an empty search
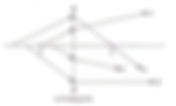
- Converging Lens – Which ray is correct after passing through the lens
Which of the following light rays behaves correctly when it passes through the converging lens? Solutions: Option C Recall these basic concepts on the 3 rays
- Displacement-time and Velocity-time Graph of Ball Thrown Up / Ball Dropped
1) When a ball is thrown up and it comes down When the ball leaves the hand, there is no upward force acting on the ball. The only force acting on the ball is its weight. This net force is opposite to the motion of the ball, hence causing the ball to decelerate. 2) When the ball is dropped and it re-bounces back (assume no energy lost) When the ball is released, the only force acting on the ball is its own weight. This net force on the ball is in the direction of the motion, hence causing the ball to accelerate as it falls. Note that the acceleration due to gravity is assumed to be 10 ms-2, where air resistance is negligible. 3) When the ball is dropped and it re-bounces back (in reality with energy lost) In reality, when the ball hits the ground, there will be some energy converted to heat and sound. So the ball will never return to its original height that it was released. So how will the graphs look like?
- 2004PPp1q15 - Volume of bubble at bottom of lake (P1V1 = P2V2)
Answer: Option A Since the air bubble is enclosed, PV at A is equal to PV at B. PAVA = PBVB (Patm + Pwater) VA = (Patm) VB (10 + 20) VA = 10 x 6 VA = 60 / 30 = 2 cm3
- Minimum force to lift a drum over a step (different examples)
Given that the mass of the drum is 20 kg. What is the minimum force, F, required to just movee th drum off the ground? (Assume uniform mass of drum and g = 10 N/kg) Knowing the position of the pivot and identifying the perpendicular distance is important. Consider the 3 variations of the same question as shown below. Type 1: Very straight forward as the pivot is same level as the CG of the drum. Hence pendicular distance is easy to identify. Type 2: Using pythagoras theorem to find the necessary perpendicular distance. Type 3: Using Toa, Cah and Soh to find the necessary perpendicular distance.
- PP N2010 P1 Q4 Two objects same size and shape but one is heavier. Motion when both released
Solutions: Option C When a body is released from rest, the only force acting on the body is its weight due to gravity . Both bodies experience acceleration due to gravity . Hence for both bodies (regardless of mass), will have the same initial acceleration of 10 m/s2. As the two bodies are of the same size and shape , they will experience the same air resistance for any particular speed . As speed increases, air resistance increases. For terminal velocity to be reached, air resistance has to be equal to the weight . Since weight is greater for the ball with larger mass, the air resistance has to be bigger. Thus, the ball has to accelerate more (air resistance increases with speed) for the larger air resistance to be equal to the weight. Hence the ball with larger mass will have larger terminal velocity . [NOTE] Do not confuse ‘speed of the body is independent of the mass’ as learned in Work Done, Energy and Power. This concept is based on the assumption that there is no air resistance. So not applicable in this question as for terminal velocity to occur, air resistance must be present.
- 2024 Specimen Paper 6091 P1 Q30 Filament bulb graphs
When comes to filament lamp, the non-ohmic characteristic properties comes to mind. But for this quesitons, you have to understand that the p.d. across the lamp remains constant. Refer to the video for explanation. Answer: Option: A
- Direction of Frictional Force on Tyre or Wheel
For these type of questions, it is important to identify which tyre/wheel is connected/powered by the engine or the person. On each tyre or wheel, there are actually two types of frictional force. Frictional force on wheel Frictional force on road/ground You can view the explanation plus the 4 examples from Olevel p1 in the video below. Examples used in the video. 2007PP P1Q5 Answer: Option D 2004PP P1Q5 Answer: Option D 2020PPp1q6 Answer: Option B 2021PP P1Q7 Answer: Option C
- Using P = I^2R and P = V^2/R to explain which component uses the highest power or energy.
Instead of P = IV to explain, it might be easier to explain using P = I^2R when the components are connected in series where current I is constant. Hence power P is directly proportional to R. The bigger the R, the more power it uses. Likewise, if the components are connected in parallel, it will be easier to use P = V^2/R, as the potential difference is constant for the components connected in parallel. Hence, power P is inversely proportional to R. The smaller the R, the more power it uses. SP2021Q8 PP2017Q11
- PP2017Q11 Using P=I^2R and P=V^2/R to explain which has higher power
Resistors may be connected in series or parallel. When asked which resistor has higher power (hence higher energy), in general we will think of using P = IV. But when using P = IV, it cannot relate to resistance R of the resistors directly. Hence it will be more appropriate for us to P = I^2R or P = V^2/R. For resistors in series , the current is the same. Hence it will be more direct to compare P and R using P = I^2R , where P is directly proportional to R . For resistors in parallel , the p.d. is the same. Hence it will be more direct to compare P and R using P = V^2/R , where P is inversely proportional to R . Refer to the video for explanation
- When a thermistor is connected in series with a fixed resistor, how to explain the p.d. varies as resistance temperature changes?
When two components are connected in series, where one is a fixed resistor and the resistance of the other can vary (e.g. thermistor, light dependent diode, variable resistor etc), you always make use of the fixed resistor to explain the its p.d. as resistance is constant. Then use the concept of sum of p.d. across both components is equal to the e.m.f of the circuit to explain how the p.d. across the other component varies . Though thermistor is not in SciPhy syllabus, it can still be tested as long as the information on thermistor is given. Refer to the videos below where 2 are from Sciphy and the other is from Pure. SP2020P2Q9 SP2013P2Q11 PP2008P2Q11OR
- 2020PPp1q9 moments – Find force P acting on stick by shoulder
Using the concepts that POM, we know 1) Ma = Mc 2) net force on the stick is 0N. Most of us will most likely to take pivot about P as default, and find F, then P using the concept of net force = 0N. But a body is in equilibrium, you can actually take pivot about any point in the body to do calculation based on Principle of Moments (POM). This method is especially using to find the answer for P straight away. The video below will guide you the normal and the short-cut. Answer: Option D
.png)